Rheumatic Disease
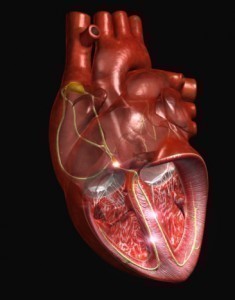
Rheumatic heart disease is a disorder in which the heart valves are permanently damaged by a bout of rheumatic fever.
Causes of Rheumatic Heart Disease
The disease will be induced by rheumatic fever that results from a streptococcus bacterial infection which is left untreated or not treated sufficiently. It may then subsequently affect the heart and cause valvular deterioration. The damage to the heart may specifically involve scarring of the heart valves which will cause the heart to pump more forcefully eventually weakening the heart over time. The damage may be temporary and heal on its own or it may be permanent and may subsequently cause congestive heart failure. Rheumatic fever is not prevalent in the United States, and typically occurs in children who had a strep infection that was not treated adequately or at all. Children within the age group of 5-15 years who are repeatedly infected with strep throat are usually at an increased risk for developing the disease.
Symptoms of Rheumatic Fever
The symptoms of rheumatic fever typically commence within five weeks of being infected with the Streptococcus bacteria. The symptoms may be slightly different for each individual however there are some symptoms that are generally indicative of rheumatic fever that may include but are not limited to the following:
- The presence of small nodules (small, hard bumbs) that will be just beneath the skin.
- A fairly sudden alteration in an individuals neuromuscular movements which may include jerky movements, slight changes in handwriting among other noticeable developments.
- Some amount of joint inflammation which may include tenderness, swelling and areas of redness on several joints. The joints that will display this symptom are generally the larger joints such as the ankles and knees. The inflammation will migrate to different joints for many days.
- Extreme tiredness or fatigue.
- Abdominal pain
- Fever
- The presence of a pink peculiar rash that may be seen on the trunk, legs and arms.
- Weight loss
Because the symptoms of the disease will look like other conditions it is important to consult a doctor to confirm diagnosis of this possibly life-threatening disorder.
Treatment for Rheumatic Heart Disease
The type of treatment that will be employed will be dependent on certain factors.
- An individual’s complete medical and health history.
- The individual’s ability to tolerate certain types of medications, therapies and procedures.
- The extent and severity of the disease.
It is best to try and prevent the development of the disease altogether because of the obvious complications that may arise. Once an individual is suspected of having strep throat treatment with antibiotics is necessary to prevent the proliferation of the streptococcus bacteria in the bloodstream. The use of antibiotics have dramatically decreased the mortality rate of rheumatic fever and heart disease. Individuals who have suffered from rheumatic fever are given a course of antibiotics daily or monthy to prevent a relapse of the disease and to lessen the risk of further damage to the heart in cases where damage occured.
Once inflammation of the heart manifests the individual is given bed rest and a course of antibiotic treatments to treat the bacterial infection.
If congestive heart failure occurs there are other medications that may have to be administered to treat it.
In cases of valvular degeneration surgery may be performed to repair or replace the faulty valve.