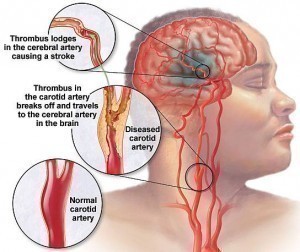
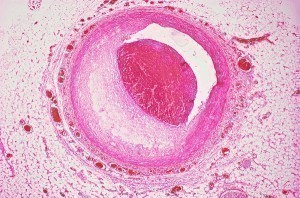
Cerebrovascular Disease
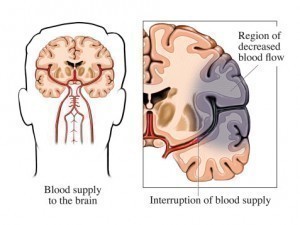
This is a group of brain dysfunctions relating to the disease of vascular tubes (blood vessels) supplying the brain. This disease is known primarily to affect elderly persons; however due the nature of the disease it can affect anyone if care is not taken to be healthy. Changes in the design of the blood vessels may make them narrow, stiff, deformed amongst other deformations, these changes in the blood vessels result in increased blood pressure in the brain since they vessels get narrower, which result in stroke and intracranial hemorrhage.
Causes of Cerebrovascular Disease
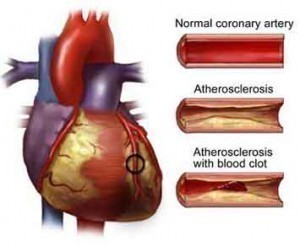
Hypertension is the most significant cause of cerebrovascular disease; it damages the blood vessel lining, and endothelium. Sustained hypertension permanently changes the architecture of the blood vessels making them narrow, stiff, deformed, and more vulnerable to fluctuations in blood pressure. Cerebrovascular Disease is also noted as being genetic , since Hypertension is can be said to be genetic.
Other known causes of Cerebrovascular Disease include obesity, stress, unbalanced diet, no exercise , along with other lifestyle practices.
Symptoms of Cerebrovascular Disease
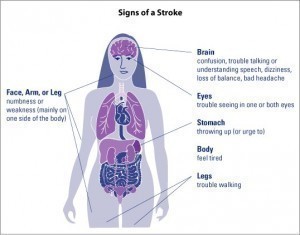
A cerebrovascular patient may display the following symptoms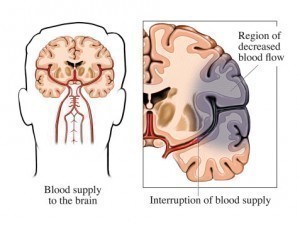
- dizziness
- nausea
- vomiting
- severe headaches
- head pressure
- numbness within the limbs
- slurred speech
- vision loss
- loss of coordination and the ability to walk
These symptoms will not all occur with everyone who suffers from Cerebrovascular disease, however when there is an attack one or more of the symptoms may present themselves. It should also be noted that some persons who have the disease show no sign of the disease.
Treatment Options
Treatment options for cerebrovascular disease include:
Medications: Blood platelet inhibitors such as Aspirin, Dipyridamole, Ticlopidine, Clopidogrel and Sulfinpyrazone are effective in reducing the risk for stroke.
Surgical Procedures: Carotid Endarterectomy: In this procedure an incision is made into the carotid artery and the plaque removed with the help of a dissecting tool thus enabling normal blood flow.
Non-Surgical Procedures: Carotid Angioplasty and Stenting: In this procedure, a balloon tipped catheter is inserted into the artery and the balloon inflated to press against the plaque so as to flatten the plaque and reopen the artery. A tiny, slender metal mesh tube (stent) is fitted inside the carotid artery to improve the blood flow in the arteries blocked by plaque.
Hemorrhagic strokes may require surgery to relieve the pressure within the brain. Another treatment, endovascular treatment, requires inserting a