Cardiovascular Disease
Definition of Cardiovascular Disease
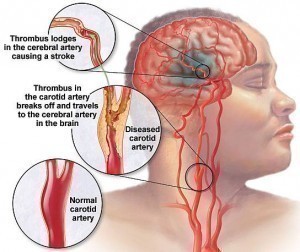
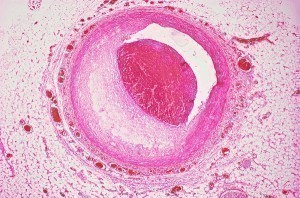
Cardiovascular disease is identified as any disease that affects the heart or blood vessels (veins or arteries). It is often specifically associated with atherosclerosis (arterial disease) despite the fact that the term in and of itself suggests any disease that affects the cardiovascular system. The incidence of this type of disease is rising progressively and kills far more Americans than cancer. Because there is a tendency for heart conditions to be asymptomatic it is necessary to employ preventive measures to lessen the risk of developing any form of cardiovascular disease. Cardiovascular diseases include aneurysm, angina, congestive heart failure, peripheral vascular disease, myocardial infarction or heart attack, cerebovascular disease and stroke.
Causes of Cardiovascular Disease
There are certain factors that increases the likelihood of developing cardiovascular disease. These factors are primarily related to lifestyle although some genetic factors will play a role in the development of these kinds of disease. The risk factors will include the proceeding.
- Going through menopause.
- Maintaining high levels of bad cholesterol and low levels of good cholesterol.
- Not partaking in sufficient amounts of physical activity especially exercise.
- A family history or genetic predisposition to acquiring the disease.
- Suffering from high blood pressure or hypertension.
- Diabetes.
- Smoking.
- Being of advanced age particularly age 40 years or older.
- Being obese or greatly overweight.
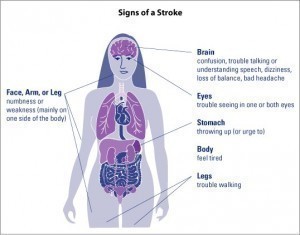
Symptoms of Cardiovascular Disease
It is not uncommon for the disease to be asymptomatic in the first phases of development. However once the disease progresses to the point where the heart has deteriorated some symptoms will become painfully obvious. These may include the following:
- Having a stroke which symptoms will appear suddenly and include: numbness in the face legs and or arm; vision problems; an extremely severe headache; general confusion with trouble speaking and understanding; dizziness and loss of coordination and balance.
- Cardiac arrest, which will customarily manifest after a prior heart attack but can occur as a primary symptom.
- Fainting
- Angina pectoris or chest pain which will not persist when resting.
- An overall feeling of discomfort.
- Shortness of breath that will normally materialize after physical activity or when lying flat.
- Being unable to sleep without two pillows or more because of breathing difficulties.
- An irregular heartbeat.
- Feeling dizzy and lightheaded
- Feeling general weakness after any kind of additional activity.
- Heart palpitations.
- Pain in the jaw, shoulder blades and left arm that is provoked by exercise or by resting.
Most cardiac disease symptoms will materialize after some type of physical activity most likely exercise. Individuals over time observe a decreased ability to function doing normal activities.
Treatment for Cardiovascular Disease
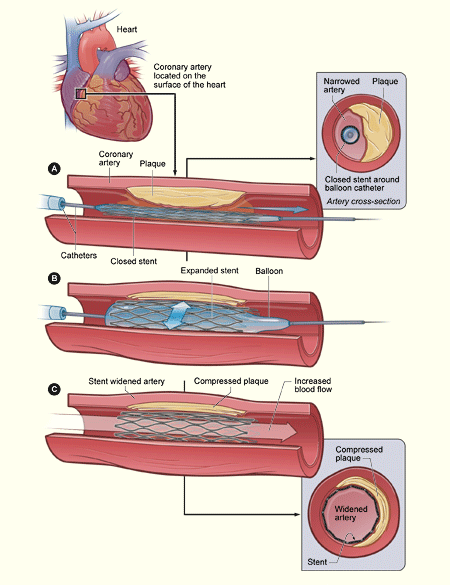
The type of treatment will depend on the disease that manifests. Treatment may include the administering of medications and surgery. The medications that will be used will generally alleviate the symptoms associated with the disease but will not be a cure for the existing condition. In some cases especially with a stroke much of the damage if severe will be irreversible. However surgery, medication and rehabilitation may improve the general prognosis. In most cases of cardiovascular disease changes in lifestyle will have a profoundly positive effect on the overall outcome. These changes may include eliminating smoking, eating healthier foods, exercising regularly, minimizing stress levels, controlling other conditions like diabetes and hypertension and maintaining an ideal body weight.
For more information on Cardiovascular Disease read: